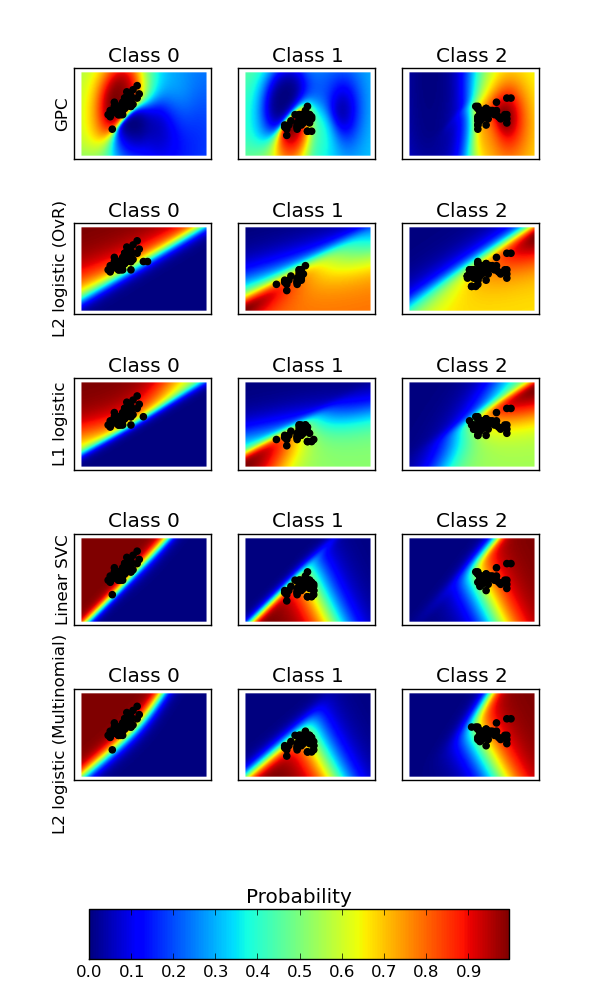
Plot classification probability¶
Plot the classification probability for different classifiers. We use a 3 class dataset, and we classify it with a Support Vector classifier, L1 and L2 penalized logistic regression with either a One-Vs-Rest or multinomial setting, and Gaussian process classification.
The logistic regression is not a multiclass classifier out of the box. As a result it can identify only the first class.
Script output:
classif_rate for GPC : 82.666667
classif_rate for L2 logistic (OvR) : 76.666667
classif_rate for L1 logistic : 79.333333
classif_rate for Linear SVC : 82.000000
classif_rate for L2 logistic (Multinomial) : 82.000000
Python source code: plot_classification_probability.py
print(__doc__)
# Author: Alexandre Gramfort <alexandre.gramfort@inria.fr>
# License: BSD 3 clause
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.gaussian_process import GaussianProcessClassifier
from sklearn.gaussian_process.kernels import RBF
from sklearn import datasets
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:, 0:2] # we only take the first two features for visualization
y = iris.target
n_features = X.shape[1]
C = 1.0
kernel = 1.0 * RBF([1.0, 1.0]) # for GPC
# Create different classifiers. The logistic regression cannot do
# multiclass out of the box.
classifiers = {'L1 logistic': LogisticRegression(C=C, penalty='l1'),
'L2 logistic (OvR)': LogisticRegression(C=C, penalty='l2'),
'Linear SVC': SVC(kernel='linear', C=C, probability=True,
random_state=0),
'L2 logistic (Multinomial)': LogisticRegression(
C=C, solver='lbfgs', multi_class='multinomial'),
'GPC': GaussianProcessClassifier(kernel)
}
n_classifiers = len(classifiers)
plt.figure(figsize=(3 * 2, n_classifiers * 2))
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=.2, top=.95)
xx = np.linspace(3, 9, 100)
yy = np.linspace(1, 5, 100).T
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(xx, yy)
Xfull = np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]
for index, (name, classifier) in enumerate(classifiers.items()):
classifier.fit(X, y)
y_pred = classifier.predict(X)
classif_rate = np.mean(y_pred.ravel() == y.ravel()) * 100
print("classif_rate for %s : %f " % (name, classif_rate))
# View probabilities=
probas = classifier.predict_proba(Xfull)
n_classes = np.unique(y_pred).size
for k in range(n_classes):
plt.subplot(n_classifiers, n_classes, index * n_classes + k + 1)
plt.title("Class %d" % k)
if k == 0:
plt.ylabel(name)
imshow_handle = plt.imshow(probas[:, k].reshape((100, 100)),
extent=(3, 9, 1, 5), origin='lower')
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
idx = (y_pred == k)
if idx.any():
plt.scatter(X[idx, 0], X[idx, 1], marker='o', c='k')
ax = plt.axes([0.15, 0.04, 0.7, 0.05])
plt.title("Probability")
plt.colorbar(imshow_handle, cax=ax, orientation='horizontal')
plt.show()
Total running time of the example: 4.16 seconds ( 0 minutes 4.16 seconds)

