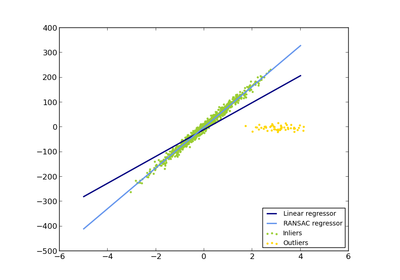
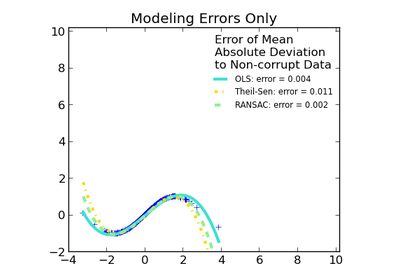
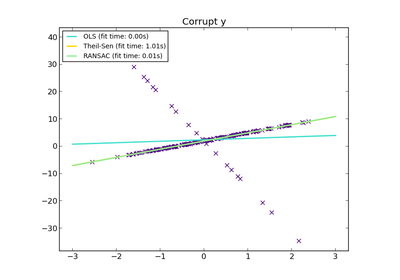
sklearn.linear_model.RANSACRegressor¶
- class sklearn.linear_model.RANSACRegressor(base_estimator=None, min_samples=None, residual_threshold=None, is_data_valid=None, is_model_valid=None, max_trials=100, stop_n_inliers=inf, stop_score=inf, stop_probability=0.99, residual_metric=None, random_state=None)[source]¶
RANSAC (RANdom SAmple Consensus) algorithm.
RANSAC is an iterative algorithm for the robust estimation of parameters from a subset of inliers from the complete data set. More information can be found in the general documentation of linear models.
A detailed description of the algorithm can be found in the documentation of the linear_model sub-package.
Read more in the User Guide.
Parameters: base_estimator : object, optional
Base estimator object which implements the following methods:
- fit(X, y): Fit model to given training data and target values.
- score(X, y): Returns the mean accuracy on the given test data, which is used for the stop criterion defined by stop_score. Additionally, the score is used to decide which of two equally large consensus sets is chosen as the better one.
If base_estimator is None, then base_estimator=sklearn.linear_model.LinearRegression() is used for target values of dtype float.
Note that the current implementation only supports regression estimators.
min_samples : int (>= 1) or float ([0, 1]), optional
Minimum number of samples chosen randomly from original data. Treated as an absolute number of samples for min_samples >= 1, treated as a relative number ceil(min_samples * X.shape[0]) for min_samples < 1. This is typically chosen as the minimal number of samples necessary to estimate the given base_estimator. By default a sklearn.linear_model.LinearRegression() estimator is assumed and min_samples is chosen as X.shape[1] + 1.
residual_threshold : float, optional
Maximum residual for a data sample to be classified as an inlier. By default the threshold is chosen as the MAD (median absolute deviation) of the target values y.
is_data_valid : callable, optional
This function is called with the randomly selected data before the model is fitted to it: is_data_valid(X, y). If its return value is False the current randomly chosen sub-sample is skipped.
is_model_valid : callable, optional
This function is called with the estimated model and the randomly selected data: is_model_valid(model, X, y). If its return value is False the current randomly chosen sub-sample is skipped. Rejecting samples with this function is computationally costlier than with is_data_valid. is_model_valid should therefore only be used if the estimated model is needed for making the rejection decision.
max_trials : int, optional
Maximum number of iterations for random sample selection.
stop_n_inliers : int, optional
Stop iteration if at least this number of inliers are found.
stop_score : float, optional
Stop iteration if score is greater equal than this threshold.
stop_probability : float in range [0, 1], optional
RANSAC iteration stops if at least one outlier-free set of the training data is sampled in RANSAC. This requires to generate at least N samples (iterations):
N >= log(1 - probability) / log(1 - e**m)
where the probability (confidence) is typically set to high value such as 0.99 (the default) and e is the current fraction of inliers w.r.t. the total number of samples.
residual_metric : callable, optional
Metric to reduce the dimensionality of the residuals to 1 for multi-dimensional target values y.shape[1] > 1. By default the sum of absolute differences is used:
lambda dy: np.sum(np.abs(dy), axis=1)
random_state : integer or numpy.RandomState, optional
The generator used to initialize the centers. If an integer is given, it fixes the seed. Defaults to the global numpy random number generator.
Attributes: estimator_ : object
Best fitted model (copy of the base_estimator object).
n_trials_ : int
Number of random selection trials until one of the stop criteria is met. It is always <= max_trials.
inlier_mask_ : bool array of shape [n_samples]
Boolean mask of inliers classified as True.
References
[R149] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RANSAC [R150] http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~belhumeur/courses/compPhoto/ransac.pdf [R151] http://www.bmva.org/bmvc/2009/Papers/Paper355/Paper355.pdf Methods
fit(X, y) Fit estimator using RANSAC algorithm. get_params([deep]) Get parameters for this estimator. predict(X) Predict using the estimated model. score(X, y) Returns the score of the prediction. set_params(**params) Set the parameters of this estimator. - __init__(base_estimator=None, min_samples=None, residual_threshold=None, is_data_valid=None, is_model_valid=None, max_trials=100, stop_n_inliers=inf, stop_score=inf, stop_probability=0.99, residual_metric=None, random_state=None)[source]¶
- fit(X, y)[source]¶
Fit estimator using RANSAC algorithm.
Parameters: X : array-like or sparse matrix, shape [n_samples, n_features]
Training data.
y : array-like, shape = [n_samples] or [n_samples, n_targets]
Target values.
Raises: ValueError :
If no valid consensus set could be found. This occurs if is_data_valid and is_model_valid return False for all max_trials randomly chosen sub-samples.
- get_params(deep=True)[source]¶
Get parameters for this estimator.
Parameters: deep: boolean, optional :
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
Returns: params : mapping of string to any
Parameter names mapped to their values.
- predict(X)[source]¶
Predict using the estimated model.
This is a wrapper for estimator_.predict(X).
Parameters: X : numpy array of shape [n_samples, n_features]
Returns: y : array, shape = [n_samples] or [n_samples, n_targets]
Returns predicted values.
- score(X, y)[source]¶
Returns the score of the prediction.
This is a wrapper for estimator_.score(X, y).
Parameters: X : numpy array or sparse matrix of shape [n_samples, n_features]
Training data.
y : array, shape = [n_samples] or [n_samples, n_targets]
Target values.
Returns: z : float
Score of the prediction.
- set_params(**params)[source]¶
Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as pipelines). The former have parameters of the form <component>__<parameter> so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.
Returns: self :