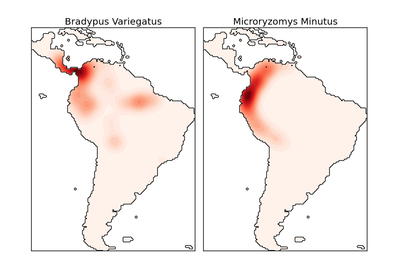
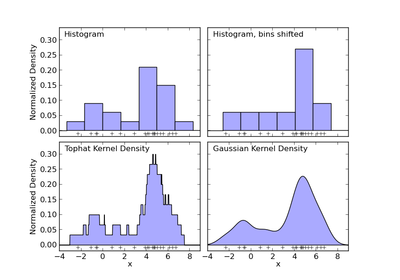
sklearn.neighbors.KernelDensity¶
- class sklearn.neighbors.KernelDensity(bandwidth=1.0, algorithm='auto', kernel='gaussian', metric='euclidean', atol=0, rtol=0, breadth_first=True, leaf_size=40, metric_params=None)[source]¶
Kernel Density Estimation
Read more in the User Guide.
Parameters: bandwidth : float
The bandwidth of the kernel.
algorithm : string
The tree algorithm to use. Valid options are [‘kd_tree’|’ball_tree’|’auto’]. Default is ‘auto’.
kernel : string
The kernel to use. Valid kernels are [‘gaussian’|’tophat’|’epanechnikov’|’exponential’|’linear’|’cosine’] Default is ‘gaussian’.
metric : string
The distance metric to use. Note that not all metrics are valid with all algorithms. Refer to the documentation of BallTree and KDTree for a description of available algorithms. Note that the normalization of the density output is correct only for the Euclidean distance metric. Default is ‘euclidean’.
atol : float
The desired absolute tolerance of the result. A larger tolerance will generally lead to faster execution. Default is 0.
rtol : float
The desired relative tolerance of the result. A larger tolerance will generally lead to faster execution. Default is 1E-8.
breadth_first : boolean
If true (default), use a breadth-first approach to the problem. Otherwise use a depth-first approach.
leaf_size : int
metric_params : dict
Methods
fit(X[, y]) Fit the Kernel Density model on the data. get_params([deep]) Get parameters for this estimator. sample([n_samples, random_state]) Generate random samples from the model. score(X[, y]) Compute the total log probability under the model. score_samples(X) Evaluate the density model on the data. set_params(**params) Set the parameters of this estimator. - __init__(bandwidth=1.0, algorithm='auto', kernel='gaussian', metric='euclidean', atol=0, rtol=0, breadth_first=True, leaf_size=40, metric_params=None)[source]¶
- fit(X, y=None)[source]¶
Fit the Kernel Density model on the data.
Parameters: X : array_like, shape (n_samples, n_features)
List of n_features-dimensional data points. Each row corresponds to a single data point.
- get_params(deep=True)[source]¶
Get parameters for this estimator.
Parameters: deep: boolean, optional :
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
Returns: params : mapping of string to any
Parameter names mapped to their values.
- sample(n_samples=1, random_state=None)[source]¶
Generate random samples from the model.
Currently, this is implemented only for gaussian and tophat kernels.
Parameters: n_samples : int, optional
Number of samples to generate. Defaults to 1.
random_state : RandomState or an int seed (0 by default)
A random number generator instance.
Returns: X : array_like, shape (n_samples, n_features)
List of samples.
- score(X, y=None)[source]¶
Compute the total log probability under the model.
Parameters: X : array_like, shape (n_samples, n_features)
List of n_features-dimensional data points. Each row corresponds to a single data point.
Returns: logprob : float
Total log-likelihood of the data in X.
- score_samples(X)[source]¶
Evaluate the density model on the data.
Parameters: X : array_like, shape (n_samples, n_features)
An array of points to query. Last dimension should match dimension of training data (n_features).
Returns: density : ndarray, shape (n_samples,)
The array of log(density) evaluations.
- set_params(**params)[source]¶
Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as pipelines). The former have parameters of the form <component>__<parameter> so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.
Returns: self :